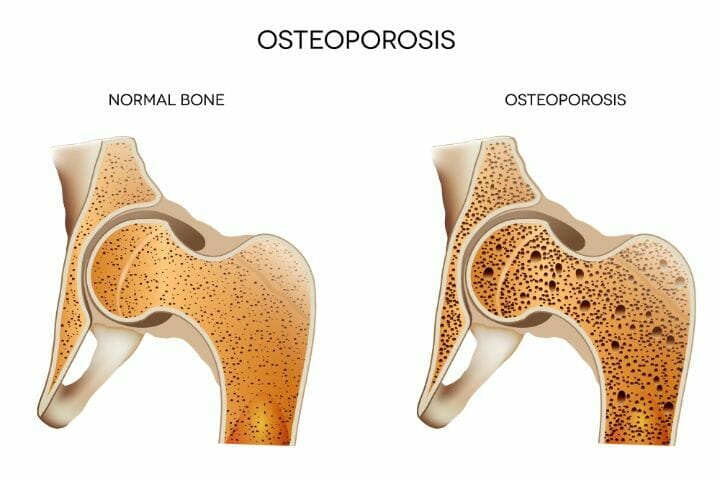
Osteoporosis is a bone infection in which the quantity and quality of the bone are lessened, leading to fractures (broken bones). Osteoporosis gives no pain or other symptoms unless a fracture has occurred.
This condition is associated with bone loss, where the bones become fragile and brittle. It can impair a person’s ability to walk and can cause prolonged or permanent disability.
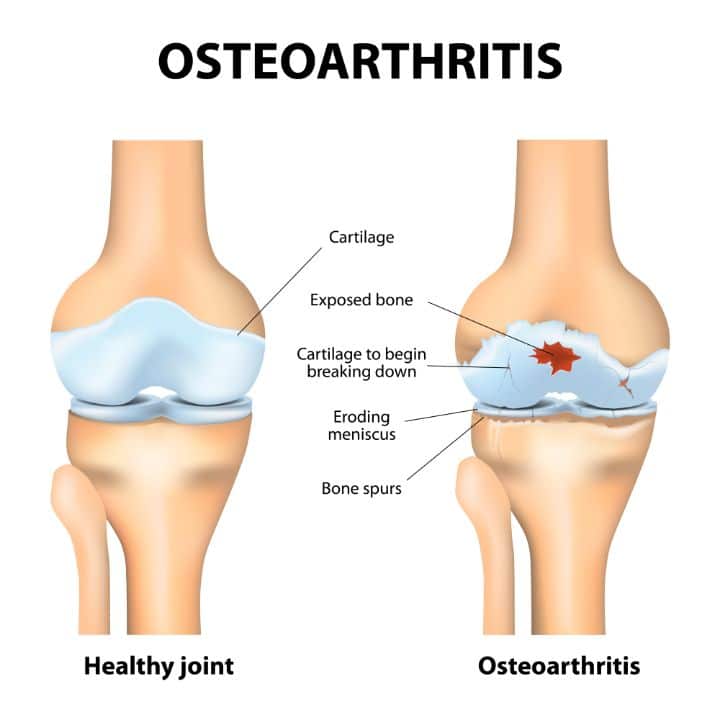
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. There is a degeneration of joint cartilage tissue along with the underlying bone and there is no associated bone loss. It is a degenerative joint infection that involves the destruction of the smooth cartilage that covers the bones, as well as changes to the bone underlying the joint cartilage.
Contents
What Is the Difference Between Arthritis and Osteoporosis?
In a normal joint structure, you have articular cartilage present between two joints. The articular cartilage functions as a lubricant that protects the joint cavity from an external shock.
Arthritis causes a break in this articular cartilage leading to bone spur and wear and tear phenomena.
It causes an inflammation or swelling of one or more joints and presents a host of joint problems; joint stiffness and joint pain with painful inflammation in the joints. Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis are two different forms of arthritis.
People who have inflammatory arthritis have an increased risk of developing osteoporosis, which is a bone-thinning disorder that can lead to frailty and fractures.
The most common form of arthritis are:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
Difference Between Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Although Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis attacks the joints, they’re very different forms of the same condition. Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune condition, while Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint condition.
Osteoarthritis as explained above, is the degeneration of joint cartilage, whereas rheumatoid arthritis is a condition in which the synovial membrane (which provides lubrication to the joint structure) gets inflamed.
The stiffness and pain of rheumatoid arthritis worsen with time as compared to osteoarthritis. Omega-3 fatty acids may have a beneficial effect in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids may have a modulatory effect on disease activity, reducing the number of swollen and tender joints.
You may also like Pros and Cons of Weighted Vest for Osteoporosis
Osteoarthritis and Osteoporosis; Severity of Pain
Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis, and the stages in the severity of pain have been termed as
- Mild pain
- Moderate pain
- Severe pain
Bone loss and bone fracture are commonly associated with osteoporosis. However, osteoarthritis also causes joint issues, and hence the joint destruction that occurs, affecting the lumbar joint and causing intense pain is common.
Signs and Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
The sign and symptoms of osteoarthritis usually differ from osteoporosis.
- Pain, mostly in hands, feet, knee, lumbar spine, and hips respectively
- Joint stiffness
- Tenderness, including swelling in joints
- Joint deformity
- Limping while walking
- Cracking sounds in the joints of knee and foot while walking
- Arthritis of the lumbar spine
You may also like Difference Between Osteoporosis and Osteomalacia
Signs and Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a silent disease as it is progressive for years and contributes to low bone density and loss in bone density.
- Fractures of bones occur, as bone strength is drastically less and bones are much fragile and brittle in this condition, resulting in fragility fracture.
- Decreased bone density
- Reduced spinal bones compression
- Extreme back pain and related pains
- Change in posture, the likelihood of lordosis and scoliosis rises
- Inability to walk properly
- Bone loss
Major Risk Factors of Osteoarthritis
The major risk factors for osteoarthritis are:
- Old age
- Joint injuries
- Repeated stress on the joints
- Obesity
- Bone deformities
- Family History
- Females going through postmenopause
- Diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus
You may also like Apple Cider Vinegar and Osteoporosis – A Complete Guide
What Are the Factors that Aggravate Osteoporosis
- Smoking
- Use of alcohol
- Fractures of bone over the age of 40
- Those with very low or very high BMI
- Postmenopausal women
- Low intake of calcium
- Low intake of vitamin D
- Conditions like hyperthyroidism
Diagnostic Procedure for Osteoarthritis
The diagnosis of osteoarthritis is very easy. It initially includes
- Discussing your family history with the medical expert
- A physical exam or procedure
- Imaging tests such as x-ray, CT scan, and MRI
- No blood test is performed as a diagnostic procedure for osteoarthritis
Diagnostic Procedure for Osteoporosis
The diagnostic procedure for osteoporosis is more or less the same as osteoarthritis. It includes
- History
- A physical exam or procedure
- Blood test
- BMD, bone mineral density test
- Bone biopsy, if required
- Conventional x-ray of a bone
The bone density test is a great way of gauging your fracture risk and eliminating chronic pain from broken bone and conditions like inflammatory arthritis, osteoporotic fracture, or degenerative joint disease.
You may also like CBD Oil for Osteoporosis – Benefits and Options
Medical and Surgical Treatment of Osteoarthritis
The basic medical and surgical treatment of osteoarthritis includes some over-the-counter pain-relieving medications such as
- NSAIDs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for instance, ibuprofen, and ansaid, are common options
- Corticosteroid injections
- Arthroscopy
- Surgical joint replacement
Medical and Surgical Treatment of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is mainly treated with the bisphosphonates such as alendronate, ibandronate, risedronate, and zoledronic acid. Osteoporosis is also surgically treated with joint replacement surgery.
Osteoarthritis and Osteoporosis Together
It is possible that a person has osteoporosis and osteoarthritis at the same time. Both diseases may cause pain and limit mobility, but the cause of this pain and the way it is treated are quite different.
Individuals who suffer from osteoarthritis and osteoporosis should seek help planning a program to manage both conditions and pay special attention to advice about exercise.
Regular weight-bearing exercise is usually recommended for individuals with osteoporosis but can be difficult to do in the presence of significant hip or knee arthritis. Keeping joints movements requires a special technique to exercise and movement. A specially trained physiotherapist can help ensure exercises are safe and beneficial for both conditions.
You may also like Living Well with Osteoporosis
Prevention of Osteoarthritis and Osteoporosis
If you are wondering can osteoporosis be reversed, we’d like to point out that prevention is better than cure and it is hard to reverse osteoporosis. Osteoporosis may be slowed through over-the-counter medications such as bisphosphonates and must be treated at an early stage.
It is a progressive degenerative disease, which can be prevented through regular exercise and appropriate supplements. You need to engage in physical activity like yoga, pilates, isometric exercises, tai chi, etc for the management of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis.
How to Manage Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. This is very painful and causes joint degeneration in major joints such as the hip, knee, feet, lumbar spine, etc. Certain steps can be taken to reduce the effects of osteoarthritis
Exercise
Regular exercise and weight-bearing exercises are important to manage osteoarthritis. Bear in mind, right exercise is very necessary to avoid any stress on the joint leading to a major injury. Physical activity is always a better cure.
Exercise Caution and Avoid Frequent Falls
Take precautionary steps to avoid frequent falls; this is especially applicable for older adults.
Reducing Your Weight
Obesity is a risk factor for osteoporosis, especially in the management of osteoarthritis in the elderly since excess weight puts excess pressure on the joints. In a recent study, if an obese person engages in physical activity and loses 5 percent of the total weight, he will see a 25 percent reduction in the symptoms of osteoarthritis.
If you are suffering from osteoporosis, the risk factor for fractures increases with the increasing age, as the bone loss increases. Osteoporosis causes loss in bone density and low bone mass, and hence the risk of injury increases.
Multiple factors which contribute to osteoporosis are not in our control. However, there are certain factors that can be taken down with appropriate measures.
The testosterone deficiency in males increases the risk of osteoporosis, whereas the deficiency of estrogen mainly increases the risk in postmenopausal women. You are at a higher risk if you:
- Have a history of previous fractures
- Have been on glucocorticoid therapy for a long time
- Have a weight of fewer than 127 pounds or 57 kg
- Have a family history of decreased bone strength and hip fracture
You may also like Does Osteoporosis Affect Teeth and Nails?
Measures to Prevent Bone Loss
There are certain precautionary measures that can be done to control osteoporosis These steps are listed below
- Cutting down the excessive intake of alcohol and sugary, carbonated beverages
- Quit smoking
- Intake of calcium supplements
- Intake of vitamin D supplements
- Physical activity that includes weight-bearing exercises
- Resistance training and pilates for osteoporosis
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis is a progressive degenerative disease, whereas osteoporosis is a brittle bone disease. Lumbar spine arthritis is common in osteoarthritis. The fractures are common in both diseases.
Osteoarthritis involves the joint cartilage, whereas osteoporosis involves the underlying bone. Both conditions can be prevented at an early stage through over-the-counter medications, bone density testing, and other relevant treatments. You can find that the condition can be treated with exercise, a healthy osteoporosis diet plan, and supplements for osteoporosis.