Smoking has detrimental effects on your body. It adversely affects your internal organs and their functioning. Among other disorders that are linked to smoking, scientific research indicates that smoking is also a for weakening, , and fractures.
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention states that around 55 million people in the United States suffer from . Moreover, it is prevalent among 200 million people worldwide.
Contents
Insights into
is a condition that affects bones, making them less dense and prone to fractures.
It causes a reduction in () leading to and in complicated cases. To sum up, is characterized by , , lesser , , and .
Apart from smoking, other factors for include:
- Family history of and .
- Small skeletal framework and
- Menopause or early menopause.
- Amenorrhea or absence of menstruation
- deficiency
- Lack of
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Prolonged use of drugs that treat asthma, thyroid deficiencies, lupus, and seizures.
can often go unnoticed as it progresses silently causing and affecting new bones with time. It is mostly diagnosed when a occurs.
Older adults between the ages of 40 to 50 are at an increased risk of as they have crossed their prime time of bones heal at a slower rate. Smokers, especially who smoke are hence, more prone to due to
Read more interesting facts about osteoporosis here.
You may also like What is the Difference Between Osteoarthritis and Osteoporosis?
How Does Smoking Cause Osteoporosis?
As mentioned earlier, studies indicate that smoking is considered a for . Smoking has already been proven to have a direct relationship with . It can affect the of an individual of any age, weaken the and cause .
Smoking affects your body’s ability to absorb calcium, leading to lower bone density and weaker bones. Nicotine slows the production of the bone-forming cells that are so crucial to healing. Tobacco causes an imbalance in bone turnover, leading to lower bone mass and making bone vulnerable to osteoporosis and fracture.
The prime time for as well as improving is from childhood till the age of 30. Adolescents smokers have an of lesser than non-smokers of the same age group.
How Does Smoking Aggravate :
Cigarette smoke contains about 7000 chemicals that are involved in premature death, various chronic diseases like chronic heart disease or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and even cancer. The free radicals in the smoke attack the body’s defense system. A chain of reactions leads to the destruction of essential components of the body, such as cells, organs, and hormones that regulate .
Research studies reveal that tobacco interacts with the skeletal system- it upsets the balanced process of turnover, leading to weaker bones with low and mass.
Tobacco causes adverse effects on bone density directly and indirectly. It directly hinders processes like angiogenesis and osteogenesis of . Nicotine and other free radicals in cigarette smoke kill osteoblasts which are -forming cells.
They also damage the blood vessels leading to a lack of oxygen supply. Due to , smokers tend to have repeated fractures and even a small fall could lead to a hip fracture. In its advanced stages, osteoporosis could be fatal.
The healing period of a is also slower compared to a non-smoker as there is decreased supply of oxygen to the -forming cells. Along with blood vessel damage, excessive tobacco damages the nerves in the toes and feet, leading to an increased risk of falls and consequent fragility fractures.
Tobacco acts indirectly on by altering body weight, sex hormones, adrenal hormones, PTH- axis, and causes elevated oxidative stress on . Estrogen in females is essential for reproduction and maintaining optimal .
The toxins in cigarette smoke cause an imbalance in and stimulate the liver to produce -destroying enzymes which speed up . This is detrimental in a with already deteriorating
Cortisol is a hormone that increases upon interaction with toxins found in cigarette smoke. It further enhances breakdown. Calcitonin is another hormone that is adversely affected by smoking.
You may also like Best Supplements for Osteoporosis
Management Strategies for
The first option for smokers to manage is to discard the habit. Putting an end to smoking always brings a positive change in an individual’s quality of life and health. The body starts to heal and increases. The earlier you stop smoking, the lesser your risk of low bone density and as you age.
A study published in the Journal of Women’s health in 2006 revealed that a group of postmenopausal women had significant improvement in after quitting smoking for a year. The results were compared with the women who continued smoking and this group was reported to have lesser
Nicotine Replacement Therapy:
Many programs help a person recover from cigarette addiction. Lozenges with nicotine, patches, gums, and prescription medicines are reliable resources to counter the addiction.
These products help the person fulfill the nicotine craving in a smoke-free way. Moreover, they are FDA-approved with the assurance that they are safe, effective, and with lesser side effects.
Chain smokers get addicted to nicotine and their body starts depending on it. The nicotine craving comes when the level of nicotine in the body decreases and withdrawals occur when the person is deprived of cigarettes. The withdrawal effects include depression, insomnia, and anxiety.
These effects can be effectively managed by nicotine replacement therapy. As the name indicates, nicotine replacement therapy provides the body the amount of nicotine required from products other than cigarettes such as lozenges, nicotine patches, and gums. The amount of nicotine can be gradually decreased till the person completely recovers from the withdrawal effects.
You may also like Difference Between Osteoporosis and Osteomalacia
and
plays a vital role in and its deficiency can lead to and . Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium. Calcium and vitamin D combination is used to treat or prevent a calcium deficiency. You can maintain strong and healthy bones by consuming a diet rich in and .
Some good sources of are dairy products with low fat, -fortified food and drinks, and dark leafy vegetables whereas can be obtained from egg yolks, liver, and fish.
The recommended amount of and increases as the individual crosses 50 as the occurs more rapidly at old age. Old age also decelerates the healing process. Therefore, the recommended is 1000mg for people aged below. For women over 50 and men over 70 years of age, the recommended calcium intake is 1200mg daily.
The intake recommended for older adults is 600-800IU every day.
Physical Exercise
Just like muscles, your bones are also positively impacted by increased physical activity. Sitting idle for prolonged periods of time can result in decreased bone mass and worsen bone health.
Weight-bearing exercises are recommended to increase and maintain the body’s . These include climbing stairs, walking, and dancing. Resistance exercises (weight-bearing exercises) like weight lifting are also effective for increased . Tai chi and Yoga are also good for osteoporosis.
You may also like Apple Cider Vinegar and Osteoporosis
Minimize :
Excess alcohol upsets the level in the body. It also interferes with the synthesis of hormones that safeguard the bones. In addition to this, alcohol also affects the vitamins that are needed to absorb . Hence, it is necessary to cut down on alcohol to manage
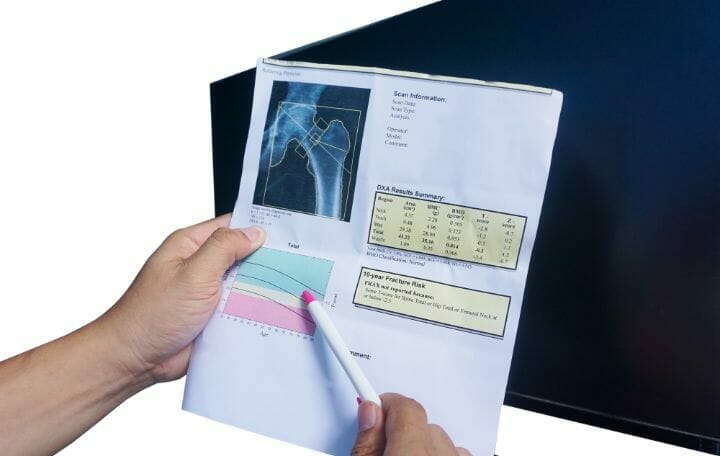
A helps you determine in various regions of the body. It is a completely painless procedure that detects before the occurrence of a .
A Dexa Scan can predict the in the individual. A person who smokes or has a history of smoking can consult his/her healthcare provider regarding a . The correct diagnosis can help your doctor choose the most suitable method of treatment for reducing the consequences and help you live well with osteoporosis.
Medication
There is a variety of medicines available to treat . A with a history of smoking can consult her healthcare provider regarding her and most suitable medicine.
At present, only the symptoms of can be managed, but there is no complete cure. There is extensive research as to whether osteoporosis can be reversed. In some research, CBD oil for osteoporosis is said to be beneficial for improving bone health.
Following the above-mentioned strategies can prevent and treat and are especially beneficial in the management of osteoporosis in the elderly.