Read our heart disease guidebook for seniors and caregivers to understand the types, causes, and precautions that you need to take if you have heart disease or are taking care of one.
Contents
Did you know that one in four deaths in the US is caused due to heart disease? Heart diseases can happen to any person with certain pre-existing conditions, genetic disorders, or other weight-related issues, lifestyle, and hormonal balance. But it is mainly seen in seniors.

Old age is a risk factor for heart diseases. Other factors that add to the burden of disease in old age may include obesity, frailty, and diabetes. Some heart diseases can be treated through medication or surgery, while others are lifelong. To learn more about heart diseases, please keep reading.
Types Of Heart Diseases
The common types or broad categories of heart diseases include:
- Coronary Artery Diseases
- Heart Failure
- Cardiomyopathy or Diseased Heart Muscle
- Arrhythmia or Abnormal Heartbeats
- Congenital Heart Defects
- Heart Infection
- Valvular Heart Diseases
Read on to know the details about common heart diseases that affect seniors.

Coronary Artery Diseases
Coronary artery diseases (CAD) are the most common heart diseases. CAD occurs when plaque forms in the arteries. Usually, this plaque is made of cholesterol, resulting in the narrowing down of arteries. So, adequate blood cannot flow through.
Causes
The primary cause of coronary artery disease is atherosclerosis or plaque build-up. However, there are several risk factors involved. Seniors with high cholesterol, blood pressure, or are overweight are at risk of developing coronary artery disease. Women become more prone to the disease post-menopause.
Symptoms
- Angina (Chest pain)
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
Treatment or Prevention
To recover from coronary artery disease, lifestyle changes are a must. These changes should include low sodium and low-fat diet and physical exercise. Cardiologists may prescribe certain medications, as well. In case of severe conditions, you may need to opt for surgery.
Hypercholesterolemia
When cholesterol and apolipoprotein B (apoB)-rich lipoproteins, also known as low-density lipoprotein (LDL), levels rise, the plasma cholesterol levels become high while the plasma triglycerides remain the same. This condition is known as hypercholesterolemia.
Causes
Causes of hypercholesterolemia include an unhealthy lifestyle, diabetes as well as hypothyroidism. Diabetic patients are also at risk. Other secondary hypercholesterolemia causes include nephrotic syndrome (chronic renal failure) and obstructive liver disease.
You may also be at risk if you have a history of drug abuse, particularly corticosteroids, anabolic steroids, and progestins.
Symptoms
- Angina
- Xanthelasmas or deposit of cholesterol on the eyelids
- Xanthomas or fatty deposits in the body
- Cholesterol deposits in different parts of the body like the elbows, under-eye area, skin, and knees.
Treatment or Prevention
Treatments of hypercholesterolemia usually involve lifestyle modifications along with statin therapy. Statin therapy can be used for older adults as well.

Heart Attack
A heart attack or a myocardial infarction occurs when the blood flow to the heart is restricted or blocked. This blockage usually occurs due to the build-up of cholesterol, fat, and other such substances. These form plaque in the arteries, clogging them and reducing blood flow.
Causes
Heart attacks occur in men of 45 years or more and women who are 55 and above. This happens due to high blood pressure, high cholesterol or triglyceride levels, and several other causes. Heart attacks may also occur due to obesity.
Metabolic syndrome may happen due to obesity, high blood pressure, and high triglyceride. Seniors who have metabolic syndrome are more likely to suffer from heart attacks than those who don’t have the condition. Older adults who have diabetes are also at risk.
Several stimulant drugs like amphetamines and cocaine can cause heart attacks. These drugs usually trigger spasms in the coronary arteries, which reduce the blood flow to the heart and cause a heart attack.
Another cause of heart attack is preeclampsia. It is a condition in pregnant women that raises blood pressure. When this happens, it increases the risk of heart attacks and cardiac damage. It can become especially threatening when you grow old.
Autoimmune conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can also trigger heart attacks.
Symptoms
- Nausea
- Indigestion
- Pressure, pain, or squeezing and tightening sensation in the chest
- Heartburn
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Cold sweat
- Shortness of breath
Treatment or Prevention
It is essential to consult the doctor if you or your caregiver notices any of the above symptoms. But heart attack symptoms are not the same for everybody. If you think a heart attack is happening, you must immediately dial emergency services. If your doctor recommends it, you can also take aspirin or nitroglycerin to ease chest pain.
Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure occurs when the blood is pumped at a slow rate and the pressure in the heart increases. The heart cannot pump the oxygen necessary, and the chambers may keep expanding to allow pumping more blood. However, this results in the chambers becoming thick and stiff. While this helps blood flow, it also causes muscle walls to weaken in the long run.
Causes
Some common causes of congestive heart failure include other heart diseases like coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, or even congenital heart defects. A heart attack or valve disease may also cause congestive heart failure.
Apart from these conditions, seniors suffering from kidney disease or diabetes are also at risk.
Symptoms
- Congestion in the lungs
- Dry hacking cough
- Wheezing
- Fluid retention
- Swelling of legs, ankles, and abdomen
- Irregular heartbeats
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Dizziness
Treatment or Prevention
While there is no cure for congestive heart failure, treatments aim to ease discomfort and reduce symptoms. Treatment or prevention of congestive heart failure involves lifestyle changes that can control the risk of other heart diseases.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) results in the enlargement of the heart muscle. In hypertrophic myocardium, the heart muscle or the myocardium thickening usually happens at the septum.
When the septum thickens, blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta reduces, which is called hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy as it obstructs the outflow of blood. Due to HCM, other parts of the heart may thicken. These include the apex, right ventricle, and left ventricle.
Causes
The causes of hypertrophic myocardium can include high blood pressure and aging. However, HCM is a genetic abnormality most of the time and is, therefore, inherited.
Symptoms
- Sudden cardiac arrest
- Heart failure
- Syncope or fainting
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Palpitations due to arrhythmias
- Fatigue
Treatment or Prevention
Cardiologists usually conduct a physical exam of the heart and lungs, along with tests like echocardiogram, electrocardiogram, exercise stress echo test, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Once the tests are done, doctors will treat the patient to reduce the severity of symptoms and ultimately prevent them altogether. Treatment will involve medications as well as lifestyle changes.

Mitral Valve Prolapse
In mitral valve prolapse, one or both of the mitral valve flaps bulge into the left atrium and do not close while the heart contracts. This causes regurgitation of blood and may result in a murmur due to turbulence in the blood flow. It is therefore also known as the click-murmur syndrome.
Causes
The exact cause of mitral valve prolapse is unknown, but it is expected to be hereditary. It can also happen due to stretchy valve flaps. This condition is also named floppy valve syndrome, billowing mitral valve syndrome, Barlow’s syndrome or myxomatous valve disease.
Symptoms
- Palpitations
- Chest pain
- Weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
Treatment or Prevention
Treatment of mitral valve prolapse depends on the patient’s medical history, symptoms, tolerance for surgical procedures, or medications. To prevent the disease from becoming severe, medications and other supportive methods like support stocking, aspirin, or warfarin therapy. But this depends on the condition of the patient.
Pulmonary Fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a severe lifelong disease that lacks an apparent cure. It is a condition caused by a combination of lung diseases that impact the respiratory system. The primary impact is on the alveoli and the connecting tissue in the lungs.
With age, the severity of the disease increases, and the lungs become hard. They do not expand as much and, therefore, cause breathing troubles.
Causes
The cause depends on the type of pulmonary fibrosis. For example, the cause of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is not known yet. But other types may be hereditary. Pulmonary fibrosis can also occur due to chain-smoking.
Symptoms
- Shortness of breath
- Dry cough
- Sudden weight loss
- Fatigue
Treatment or Prevention
There is no cure, and your cardiologist cannot reverse pulmonary fibrosis. However, a doctor can ease symptoms through oxygen therapy, medications, pulmonary rehabilitation, or lung transplant. These methods usually aim to improve the quality of life.
Atrioventricular Canal Defect
Atrioventricular canal defect or atrioventricular septal defect is usually a combination of heart diseases that affect the central region of the heart. It is a congenital heart defect. In the case of this particular disease, there is a hole in the middle of the heart chambers, along with the presence of issues with the valvular functions. The disease may become severe in old age, resulting in complications.
Causes
Since this is congenital, the causes of atrioventricular canal defects are usually related to the mother’s conditions at the time of pregnancy. Suppose the pregnant mother has diabetes, develops any viral infection like measles or rubella, or drinks and smokes. In that case, the baby has a chance of developing an atrioventricular canal defect. Babies with down syndrome are also at risk.
Symptoms
- Rapid breathing
- Lack of appetite
- Pale skin
- Fatigue
- Excessive sweating
- Bluish discoloration of skin and lips
- Edema
Treatment or Prevention
Diagnosis of atrioventricular canal defects is made through prenatal tests or physical tests after birth. Surgery is necessary to treat atrioventricular canal defects. However, if it triggers any other heart condition, you will need to consult the doctor for additional medication.

Causes And Risk Of Heart Disease
Seniors and their caregivers need to be aware of the causes and symptoms to take the correct preventive measures or consult the doctor. It is also necessary to understand the risk of heart diseases.
Let’s first understand the causes
Coronary Artery Disease
- Atherosclerosis or the build-up of fatty plaques in the arteries
- Lifestyle issues like inadequate exercise and improper diet
- Smoking
Cardiomyopathy
There are three types of cardiomyopathy: dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and restrictive cardiomyopathy.
The causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include:
- Reduced blood flow to the heart
- Toxins in the bloodstream
- Infections
- Medications, particularly those used to treat cancer
Dilated cardiomyopathy usually occurs due to the enlargement of the left ventricle, which results in less blood being pumped. While the above causes are common, several cases of dilated cardiomyopathy in seniors can be idiopathic or due to genetic disorders.
The causes of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy include:
- High blood pressure
- Old age
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may also be passed down from parents or other family members.
The causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy include:
- Loss of elasticity in heart muscle
- Connective tissue disorders
- Amyloidosis or the build-up of abnormal proteins
The loss of elasticity causes the heart muscle to become rigid. However, there is no apparent cause for this.
Arrhythmia
- Coronary artery disease
- High blood pressure
- Drug abuse
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Congenital heart defects
- Excessive intake of caffeine or alcohol
- Stress
- Valvular heart disease
- Specific dietary supplements or over-the-counter medications
In people, including seniors, with healthy hearts, arrhythmias occur due to sudden electrical shocks, drugs, and other such triggers. Therefore, caregivers should keep an eye on the medications and the doses an older adult is taking.
In diseased hearts, arrhythmias develop due to the poor functioning of electrical signals, which may not start or move through the heart properly.
Valvular Heart Diseases
- Infectious endocarditis
- Rheumatic fever
- Connective tissue disorders
While these are some common causes of valvular heart disease, you may even be born with it. If you notice symptoms like fatigue, irregular heartbeats, shortness of breath, chest pain, and syncope, you should consult the doctor.
Heart Infection
Heart infection is usually caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites that reach the heart muscle. If you have a heart infection, you will notice symptoms like fever, swelling in the legs and abdomen, shortness of breath, dry cough, skin rashes, and fatigue. You may even notice a change in your heartbeat.
Congenital Heart Diseases
Congenital heart diseases occur when the baby is still in the womb. The cause of these diseases or defects is yet to be determined. However, research suggests that other medical conditions, genetic make-up, and even the effect of certain medications can cause congenital heart disease.
Now let’s take a look at the risk factors that contribute to each of the following heart diseases.
Coronary Artery Disease
- High LDL cholesterol
- Low HDL cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
Cardiomyopathy
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- Family history of heart failure, cardiomyopathy, or cardiac arrest
- Chemotherapy drugs or radiation
- Alcohol disorder and drug abuse
Arrhythmia
- Pre-existing heart conditions
- Old age
- Diabetes
- Asthma
- Sleep apnea
- Thyroid disorder
Valvular Heart Diseases
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Rheumatic fever
- Insulin resistance
- Obesity
- Smoking
Heart Infection
- Old age
- Illegal IV drug use
- Damaged heart valves
- Bad dental health
Congenital Heart Diseases
- Rubella during pregnancy
- Smoking
- Alcoholism
- Diabetes
High Blood Pressure And Hypertension
High blood pressure can lead to hypertensive conditions. Older adults, especially those above 45 with conditions like diabetes, obesity, or high cholesterol, are at risk of hypertensive heart disease.
Hypertensive heart diseases include:
- heart failure
- Ischemic heart disease
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
In hypertensive heart diseases, to compensate for the decrease in pumping power, the chambers keep stretching to hold a larger blood volume. As this continues, the muscles weaken.
Due to this condition, the kidneys retain more sodium and fluids. As the deposits increase, the excess fluids accumulate in the feet, ankles, lungs, and other organs, resulting in congestive heart failure.
Hypertension may cause ischemic heart diseases where the arteries harden, which is also a result of atherosclerosis. While nausea, fatigue, and dizziness are common symptoms, older adults may also suffer from acute chest pains that spread over to the back, arms, neck, and jaw and irregular pulse. High blood pressure can also cause ventricular hypertrophy.
Caregivers should monitor their patients to see any signs of hypertension. Regular checking of the blood pressure at home can help keep track of pressure fluctuations. It is best to consult a doctor if you notice irregularities.

Secondary Hypertension
Secondary hypertension is a condition where the blood pressure increases due to some other disease. These include kidney diseases, thyroid issues, adrenal diseases, and obstructive sleep apnea.
Secondary hypertension may also occur due to the side effects of medications like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), contraceptive pills, diet pills, stimulants, or immune system suppressants.
The symptoms of secondary hypertension include:
- Cushing’s syndrome usually includes purple striations on the abdominal skin, abnormal body hair growth, and weakness
- Conn’s syndrome is also known as primary aldosteronism. It causes the potassium levels in the body to drop, resulting in long-term weakness
- Pheochromocytoma or tumor of adrenal gland tissue presents with flushing accompanied by an increased rate of heartbeats, anxiety, and headache
- Thyroid issues along with fatigue. Seniors suffering from thyroid conditions may also experience sudden weight loss or gain and develop intolerance towards the cold or the heat
If, as a caregiver, you notice any of these symptoms, you need to advise your patient to visit a doctor. Doctors will usually conduct the following tests to diagnose secondary hypertension.
- Creatinine test
- Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) test
- Thyroid function test
- Testing of potassium and calcium levels in the blood
Cholesterol And Heart Disease
Cholesterol is of two types: high-density lipoproteins (HDL) and low-density lipoproteins (LDL). HDL is often known as the “good cholesterol.” It collects cholesterol from the body and transports it to the liver. LDL, on the other hand, carries cholesterol wherever it is required.
But in doing so, LDL cholesterol deposits may increase, particularly in the arteries. This causes a blockage that may result in heart disease.
High levels of LDL cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease. Therefore, it is recommended that patients maintain a higher level of HDL and a lower LDL level.
What To Expect With Open Heart Surgery
Heart surgeries have evolved over time and hardly require any wide incisions on the chest. Open heart surgery is usually recommended in those suffering from coronary heart disease.
Here’s what to expect when you opt for open-heart surgery.
- The doctor will ask for your medical history and details about ongoing over-the-counter medications as preparation for the surgery.
- Two weeks before the surgery, you will need to stop smoking and drinking alcohol. You will also have to stop taking blood-thinning medications like aspirin or ibuprofen. It is essential to do so to avoid complications related to withdrawal.
- Before surgery, you will have to use a special antibacterial soap.
- During surgery, you will be given general anesthesia.
- Once the surgery is complete, you will have a couple of tubes attached to your heart.
- You will also have intravenous (IV) lines for fluid supply and a catheter for urination.
- Machines will continue to monitor the condition of your heart for a few days.
- Recovery will involve incision care, pain management, and rehabilitation.
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
Coronary artery bypass grafting is a procedure that is done to ensure proper blood flow to the heart when coronary arteries become narrow or get blocked. During the surgery, cardiologists use blood vessels from other body parts and connect them to the blood vessels above or below the narrowed or blocked artery.
A coronary artery bypass graft helps lower the risk of complications from ischemic heart diseases. After the surgery, a heart-healthy lifestyle and medications can help prevent recurring symptoms.
Heart Valve Replacement
Heart valve replacement is necessary when the heart valves become stiff from infection or old age. Rheumatic fever and staph can cause infection and result in leaky valves. If the condition is severe, the cardiologist will opt for valve replacement instead of repair.
Heart valve replacement is open-heart surgery, and the cardiologist will make an incision in the middle of the chest. However, in recent times, less invasive methods have been developed.
Heart valve replacement is necessary if you experience:
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Palpitations
- Breathing difficulty
- Edema
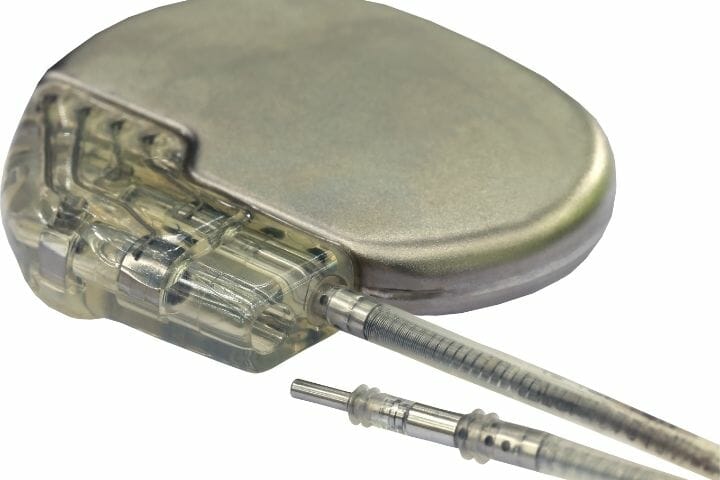
Pacemakers
Pacemakers help to control heart rhythms. A pacemaker is a small implanted device, usually to ensure that the heart is not beating too slowly. Pacemakers are generally of three types: single chamber pacemaker, dual-chamber pacemaker, and biventricular pacemaker.
You may have bradycardia or a slow heartbeat if you suffer a heart attack. This is when the cardiologist will implant a temporary pacemaker. If you suffer from chronic irregular heartbeats or slow heartbeats, you will need a permanent one. Pacemakers can help to prevent heart failure.

Carotid Endarterectomy
Carotid endarterectomy or carotid artery surgery is necessary to remove plaque build-up in the carotid artery. The surgery is essential to ensure that blood flow is normal. Your doctor may recommend carotid endarterectomy if an ultrasound shows a blockage that may cause a stroke.
Cardiac Ablation
Cardiac ablation is a procedure that helps correct heart rhythm abnormalities (arrhythmias). During this procedure, the cardiologist will introduce radiofrequency energy (heat) or opt for cryoablation (extreme cold) and create small scars in the heart to prevent irregular electric signals. This restores normal heartbeat.
Cardiac ablation is necessary when
- Increased risk of cardiac arrest
- Medications are insufficient to treat the arrhythmias
- Medications are unsuitable for the patient
It can also help if the patient develops specific arrhythmias like supraventricular tachycardia or the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.

Cardiac Rehabilitation
Patients who suffer from a heart attack or similar heart problems require special care to recover. They can get this through an outpatient program customized to their needs. Cardiac rehabilitation or cardiac rehab is precisely that. It is an outpatient program that features exercise and offers the knowledge required to recover correctly.
A cardiac rehabilitation program will usually include:
- Exercise and training
- Information about necessary lifestyle changes
- Heart-healthy diet
- Emotional support
Cardiac rehabilitation is suitable for people with different types of heart diseases. Doctors often recommend cardiac rehab after the following surgeries.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery
- Heart or lung transplant
- Angioplasty
- Stents
- Repair or replacement of heart valves
While cardiac rehabilitation is customized according to the patient’s needs, it is not always suitable for all. Suppose you are part of a health team for a patient with heart disease or a caregiver. In that case, you must analyze the patient’s ability to sustain the program. As exercising is a part of the program, patients who are not very active can sprain or strain their muscles and injure themselves.
To prepare for cardiac rehabilitation, you will have to:
- Ask your doctor to recommend a good program.
- Work out the costs and check if you have enough insurance to cover the rehab.
- Choose a specific set of attainable goals.
- Talk to your health or treatment team and case manager so that they can track your recovery.
There are several phases of cardiac rehabilitation, and for the best results, you will have to go through them all. These are:
- Clinical phase which is immediately after the cardiovascular event or surgery
- Outpatient phase during which caregivers and health teams will focus on comorbidities, limits in physical function, and participatory restrictions
- Post-cardiac rehab phase mainly involves independent monitoring of yourself
After all, phases are complete, your quality of life will improve, and there will be a significant reduction in further healthcare costs.
Managing Medication For Heart Patients
If you are a caregiver, you will need to understand what medications can be prescribed and how your patient needs to take them. Patients who manage the recovery on their own also need to be aware of the medicines and their side effects.
Following is a list of medicines prescribed to those recovering from heart diseases.
- Beta-blockers
- ACE inhibitors
- Antithrombotics
- Statins
Other medications include vasodilators, diuretics, calcium channel blockers, warfarin, and digoxin.
For proper management of medications, you should consult your cardiologist and get a fair idea of when to take the medicines. Stick to a schedule and monitor all conditions. If there is any sudden change or reaction, mainly due to the side effects, consult your doctor.
Heart Disease Prevention
Since heart disease is a risk in seniors, the only way to prevent it is to lead a healthy lifestyle. It would be best to incorporate heart-healthy diets and exercise into your everyday routine to stay fit and healthy.
You should also be aware of any changes in your body, particularly related to your heart. It is best to treat hypertension at its earliest than let it have any severe effects on your heart health. As you grow older, you can also get a few medical tests to confirm that your heart is in good condition. These tests will help catch the early signs of heart disease and thus help treat or prevent it.
Heart Healthy Habits
Certain healthy habits can help you stay fit and avoid heart diseases.
Getting Adequate Physical Exercise
Physical exercise can help you prevent heart disease. To stay fit, you can take brisk walks, go bowling, dance and cycle. Seniors who have a primarily sedentary lifestyle can begin with gardening before doing other physical activities.
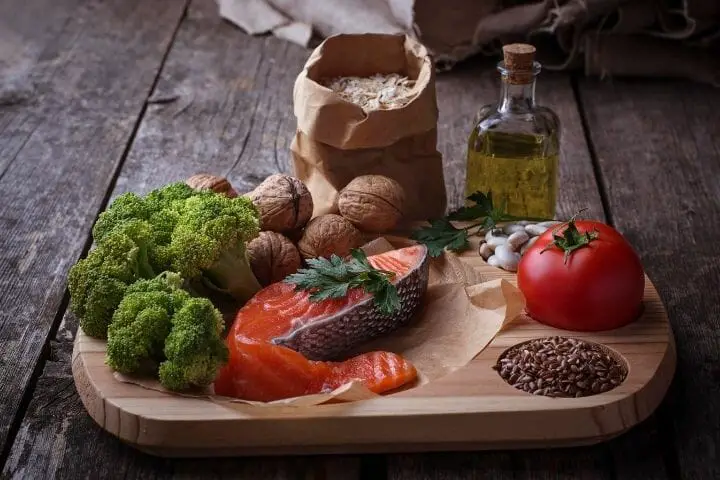
Following a Heart-Healthy Diet
A heart-healthy diet is low in saturated fats, added or processed sugar, and salt. Such a diet helps maintain low cholesterol levels and thus, lower the risk of heart disease. You can lower blood pressure and cholesterol and promote heart health with a proper diet.

Maintaining Steady Weight
Weight fluctuations can often affect your body and lead to heart diseases. Therefore, you need to balance the calories you are consuming. It is also essential to maintain a steady and proper intake of nutrients. This will help you ensure that your body weight does not fluctuate.
Not Smoking
If you smoke, it is wise to quit as you grow older. Smoking affects the artery walls and can cause irreparable damage. Therefore, it is best to stop.
Laughter And Healthy Heart
Laughter as a possible medication for heart conditions and stress is not a myth. Laughing out loud has both short-term and long-term benefits. While short-term benefits usually include stimulation of the lungs and heart muscles, long-term benefits can help reduce stress drastically.
This will help you maintain a healthy heart. When you laugh, your body will increase and decrease the stress response. The upside to this is that your heart rate also increases a bit before reducing. This is why you feel relaxed after a long laugh. So laugh with your friends and family and have fun. It will do wonders for your heart and body!
Heart diseases can affect any population, and people of every. But for seniors, they can be fatal as the other bodily functions are often compromised. Therefore, you must take precautions. Lead a healthy lifestyle, get tested, and use the above guide to stay fit. Don’t forget to leave a comment and share this information with your peers and family members.

Wrap Up
We hope our guide gave you all the information that you need to understand heart disease, its types, symptoms, causes, risk factors involved, and ways in which it is treated or prevented. This guidebook can be a one-stop shop for you to refer to in case you are taking care of multiple heart patients.
Please feel free to share any information that we might have missed out or which you might like to get added to this guide. If you loved the content, please share it with others and give us a mention on your social media sites. Your word of encouragement goes a long way in helping us write these information repositories which will hopefully help many like you!
