Let us understand how the causes of US deaths have changed over a century, which gives us a clear picture of the huge scientific victory that we have achieved through the hard work and dedication of those involved in the healthcare industry.
Contents
The leading causes of death have drastically changed from 1900 to the present. Besides the steady decline in the overall mortality rate in the US, there is a change in demographic and socioeconomic groups, like women living longer than men and whites living longer than African-Americans.

The majority of countries have seen a rapid decline in mortality rate over the last 100 years, and the US has been a leading light in this direction. The US has enjoyed more longevity than death in the past 100 years. 100 years back, one out of 40 was the annual death rate, but over time, it has decreased to 1 out 140 in the twentieth century.
Along with the decline in mortality rate, different causes of death have changed from 100 years back to the present. There could be many reasons for such reduction. In the early ’20s, more healthcare facilities and better nutrition led to lower chances of death caused due to infectious diseases.
In this article, let us understand more about significant causes of US mortality in the last 100 years, and the ways in which various diseases have been brought under control
Major Causes of US Mortality in the Past 100 Years
In 1900, the deadliest infectious diseases became the primary reason for mortality. Tuberculosis, pneumonia, flu, and gastrointestinal infections were the leading infectious diseases that brought death.
Since the impact of such infectious diseases has reduced, the top reasons for mortality have changed to heart disease, cancer, diabetes, respiratory diseases, and Covid. No matter the reason behind death, the mortality rate has declined from 1099 per 100k to Just 613 per 100k, a decline of 44%.
With various changes in health sectors and the medical industry, studies have shown a dramatic decline in deaths caused due to infectious diseases in 2020.
Leading causes of death in 1900 and 2020
| Cause of death | 1900 | %age | 2020 | %age | |
| Pneumonia or influenza | 202.2 | 18% | 13 | 2% | |
| Tuberculosis | 194.4 | 18% | – | – | |
| Gastrointestinal infections | 142.7 | 13% | – | – | |
| Heart disease | 137.4 | 13% | 168.2 | 27% | |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 106.9 | 10% | – | – | |
| Nephropathies | 88.6 | 8% | 12.7 | 2% | |
| Accidents | 72.3 | 7% | 57.6 | 9% | |
| Cancer | 64 | 6% | 144.1 | 24% | |
| Senility | 50.2 | 5% | – | – | |
| Diphtheria | 40.3 | 4% | – | – | |
| COVID-19 | – | – | 85 | 14% | |
| Stroke | – | – | 38.8 | 6% | |
| Chronic lower respiratory disease | – | – | 36.4 | 6% | |
| Alzheimer’s disease | – | – | 32.4 | 5% | |
| Diabetes | – | – | 24.8 | 4% | |
| per 100,000 population | 1099 | 613 |
Source: Statista
Decline in Mortality Rates across Leading Causes of Death
As you can see in the chart below, there has been a significant decline in mortality rates across all leading causes of death:
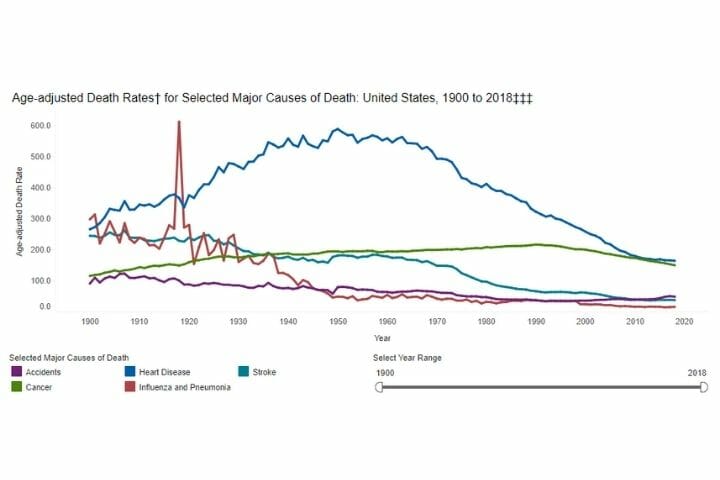
Source: CDC, NCHS
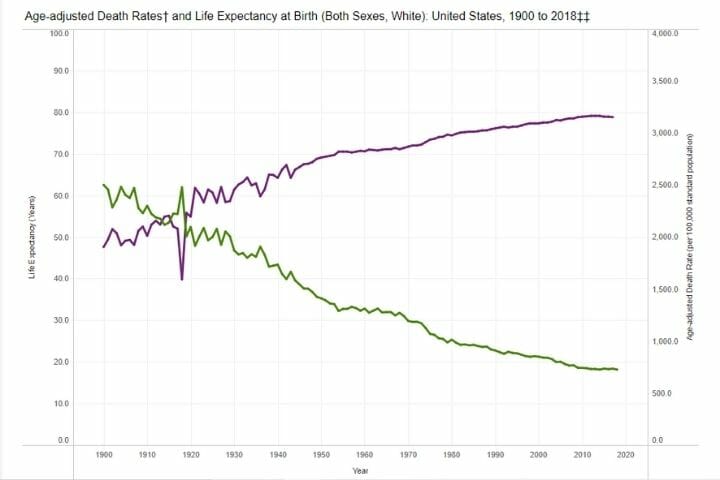
Life Expectancy and Death Rates by Race
A significant difference is visible when you compare age-adjusted death rates and life expectancy between the white and black populations. While both these parameters were very poor for African Americans in the 1900s, there was a significant improvement post removal of segregation and as race-related prejudices started to recede in the ’60s and 70s.
Death Rates and Life Expectancy: Whites
Death Rates and Life Expectancy: African-American
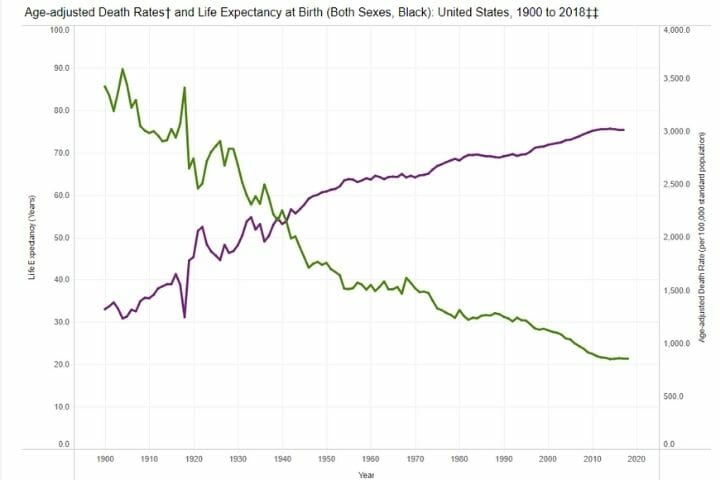
Source: CDC, NCHS
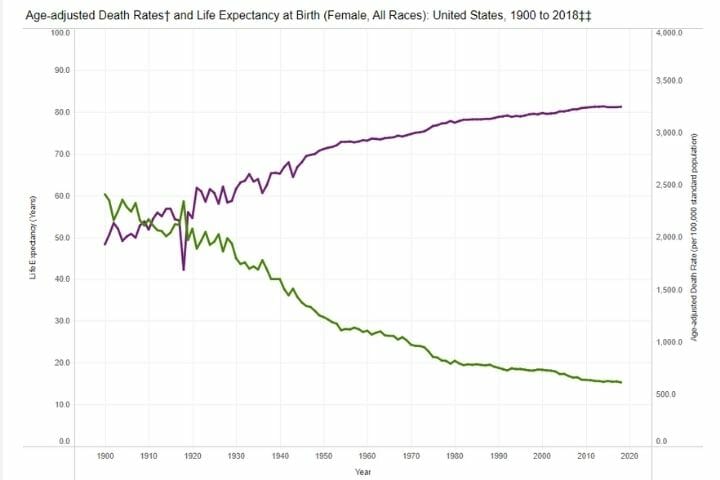
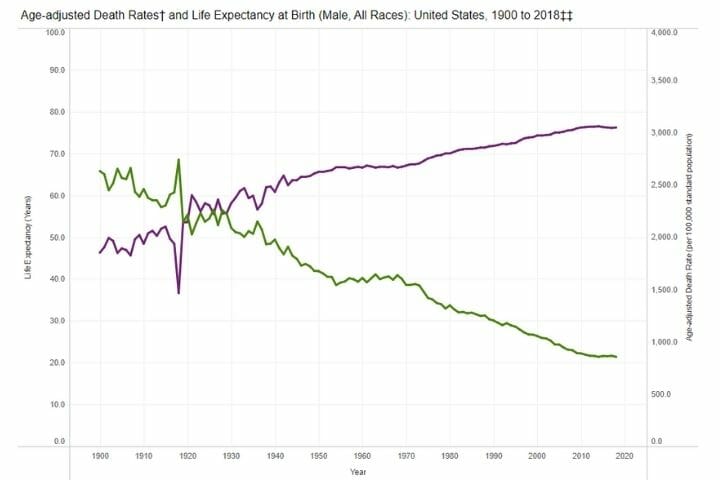
Life Expectancy and Death Rates by Sex
As you can see from the charts below, both parameters have drastically improved for women, whereas there is a lot of scope for improvement in the case of men.
Death Rates and Life Expectancy: Females
Death Rates and Life Expectancy: Males
Source: CDC, NCHS
Death Rates by Age Group
Another starting data point is the concentration of mortality. While in the 1900s, the major age group facing mortality was newborn infants, today more than 70% of those dying are part of the age group of 65 and above.
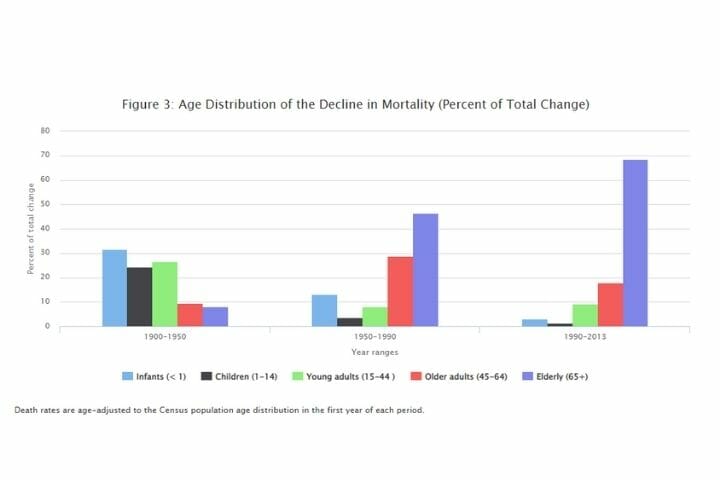
Source: University of Pennsylvania Wharton
You might also like to read: Aging Statistics – All You Need to Know
Measures Taken to Control Various Diseases From 1900 to the Present
The decline in mortality rate in the US has contributed to a major drop in child and infant mortality and has added 30 years more to the life expectancy. Despite overall progress in the mortality rate, a major change was seen in the 20th century.
In the 20th century, public health actions were considered based on 19th-century data, where the discovery of microorganisms led to major diseases and death. Such diseases were controlled by hygiene and sanitation.
Also, the discovery of vaccinations and antibiotics has shown a great decline in the death rate among children. Here are the measures that have been taken to control the death rate in the 20th century.
Sanitation and Hygiene
In the 19th century, the majority of the population had shifted from country to city; this immigration and introduction of industrialization led to overcrowding in cities. Such overcrowding leads to poor housing due to inadequate water supply and waste disposal systems.
This poor sanitation caused many diseases to adults as well as children; such diseases are typhoid, fever, influenza, tuberculosis, cholera, and malaria.
This public health concept focused on preventing infection diseases by providing clean water and proper sanitation. However, the public sector started taking measures against this in the 19-century only and continued to the 20th century.

Local and state governments have done their best to improve sanitation and hygiene. The states have developed certain health departments to undergo the concept and take care of proper sanitation and hygiene in the area they are allocated.
The first health department of the county was established in 1908. Over time, the state public health department has shown progress in controlling the diseases by incorporating various activities like the safety of food items, waste disposal system, water treatment, and providing information about personal and public hygiene.
The health departments introduced a few methods to provide safe and clean water, like chlorination and other treatments to clean the water. These methods led to a decrease in water-borne diseases and further controlled the death rate caused due to diseases caused by poor sanitation and hygiene.
Even TB-controlled plans were taken into action in the 19th century, and it is still in existence in the 20th century with more advancements. In 1900, 194 out of 1,00,000 people died from TB. Most of them lived in urban areas. The death rate due to TB decreased to 64 per 1,00,000 in 1950 from TB due to antibiotic therapy.
Another action considered in terms of sanitation and hygiene is pest control to prevent diseases caused by mosquitos or other insects. Animal and pest control played a major role in preventing diseases like rabies, malaria, plague, and more.
Mosquito-controlled programs play a vital role in preventing malaria.
Plague is a known infectious disease caused by inhalation of droplets from coughing patients. Even plague was diminished through vector control activities.
Vaccination
Smallpox, mumps, measles, tetanus, and diphtheria were common diseases in the US in the 19th century. But over time, the state government and a medical board have started vaccination programs to eliminate these diseases. Such vaccination programs were aimed at poor children. With the introduction of licensed diphtheria and tetanus vaccination in 1949, diseases among children were controlled.
The success of the vaccination program in the 20th century was taken as a concept of disease eradication. After a long vaccination campaign, the small box was diminished worldwide. Even polio was eradicated in 2000.
Antibiotics
The first-ever medical product, Penicillin, was developed in the 19th century to provide quick and reliable treatment for various bacterial diseases. Earlier, this medicine was used by soldiers to heal their wounds and treat their sickness.
Antibiotics have saved many lives from 1900 to the present. Many drugs were also developed to treat viral infections like herpes, fungal infections, parasitic diseases, and many more.
Technological Advances in Monitoring Infectious Diseases From 1900 To Present
With the advancement in technology, an increased number of detecting, monitoring, and diagnosing devices were developed to deal with infectious diseases. Even the development in the early 20th century led to the introduction of serological testing, and the recent development was molecular assays.
With the use of computers and other ways of communication over the decades, it has become easier to gather and analyze data regarding disease surveillance.

Serological Testing
In the 1910s, serological testing was introduced, and it became the only method to diagnose or control infectious diseases. It was hard to diagnose and control various diseases like gonorrhea and Syphilis. With Serological testing all around the world, it became easier to facilitate the diagnosis of syphilis or other various infections.
Viral Isolation and Tissue Culture
In the late 19th century, the first viral isolation technique came into existence. Such a technique used small sieves to strain infected material and inoculates test animals to show the substance retained to control disease-causing activity.
The first-ever filtered virus was the tobacco mosaic virus. Also, the yellow fever virus was filtered by US Army Command.
Molecular Techniques
Molecular techniques can increase the capacity to control the transmission of various threats and find new ways to treat them. During the late 20th century, molecule biology has introduced many effective tools to detect and characterize various infectious pathogens.
With the use of nucleic acid hybridization and sequencing techniques, it became easier to detect causing agents of various diseases like Hepatitis C, AIDS, and many more.

A Few Final Words
Understanding the history of our mortality and how far we have come in just a hundred years is not just an exercise in self congratulation. There are several lessons to be learnt from this data, and how various technological and scientific advancements have created an impact on the lives of people.
It guides us towards greater research funding for efforts to eradicate major diseases, and the benefits of keeping a scientific and rational approach towards medicine.
